We’re all aware that Achalasia Cardia is a rare esophageal disorder that causes difficulty eating and drinking. Even so, patients with this condition frequently struggle to swallow food and suffer from food regurgitation, which has an impact on their daily lives.
If you suffer from the same issue, it can lead to more serious complications, such as esophageal dilation. Let’s learn about this condition and its treatment with an achalasia cardia specialist, as well as how to handle its symptoms in order to improve our daily lives.
What is Achalasia Cardia?
Achalasia cardia is a rare and common esophageal condition characterized by difficulty swallowing, food regurgitation, or chest pain, which can progress to esophageal dilatation and other problems.
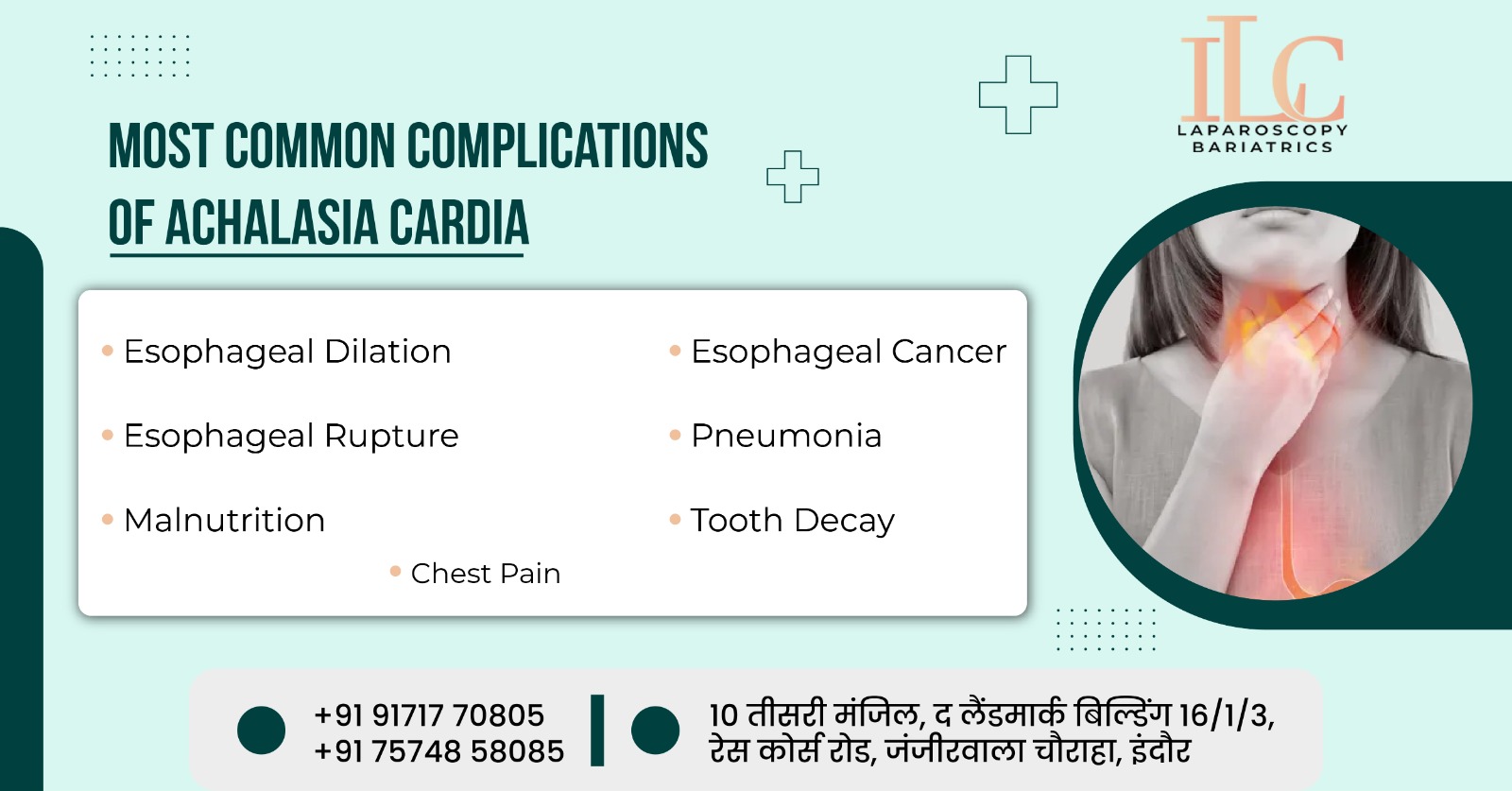
What are the Primary Complications of Achalasia Cardia?
The following are the most prevalent primary complications of untreated Achalasia cardia:
- Esophageal Dilation: Esophageal dilatation is the most prevalent complication. It occurs when the esophagus swells abnormally as a result of prolonged food and fluid retention.
- Aspiration Pneumonia: In this situation, regurgitated food (swallowed food) and liquids enter the lungs, leading to lung infections and also causing aspiration pneumonia.
- Esophagitis: In this condition, the esophagus becomes inflamed as a result of prolonged intake of food and fluids, causing irritation and probable ulceration of the esophageal lining.
- Malnutrition and Weight Loss: This scenario gets worse by the difficulty in swallowing, which causes us to fear and stop eating. This leads to a nutritional deficit and weight loss.
How Do We Treat Achalasia Cardia?
Achalasia Cardia therapy options include preventing or managing esophageal dilatation. The choice of treatment is determined by the patient’s age, overall health, and the severity of the ailment. Common Achalasia Cardia therapies include:
Pneumatic dilation: Pneumatic dilation involves inserting a balloon into the Lower Esophageal Sphincter (LES) to open it up. It can significantly alleviate symptoms while preventing further esophageal dilatation.
Heller myotomy: Heller myotomy is a surgical treatment that involves cutting the muscles of the LES to help food flow more easily.
Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy (POEM): This minimally invasive endoscopic method involves severing the LES muscle through the mouth, providing an effective and less invasive alternative to standard surgery.
Botulinum Toxin Injections: Botox injections into the LES may relieve symptoms by relaxing the sphincter muscle, but further treatments may be required.
Esophageal dilatation is the most common and serious consequence of achalasia cardia. Prompt and effective therapy for achalasia cardia is critical to minimizing complications and increasing patients’ quality of life. With advancements in both surgery and non-surgical treatments, controlling Achalasia Cardia and its complications has become increasingly effective, giving hope to people plagued by this difficult disease.